Best List of Research Proposal Topics From Our Experts
Creative Research Proposal Topics Description: Our article contains the latest research proposal topics that you have not seen anywhere else. If you don't know how to write a study, our experts have prepared a writing guide. Best List of Research Proposal Topics From Our Experts
Students are always looking for an exciting research topic. We know how difficult it is to decide what to write about on paper when there are no ideas. But we have created topics to write about research that affects all sciences. Here you will find such topics from our experts:
- Political Science Topics;
- History topics;
- Literature Topics;
- Business Topics;
- Education Topics;
- Psychology Topics;
- Philosophy Topics;
- Medical Topics;
- IT Topics;
- Biology Topics.
What are the features of our themes? Indeed, you think that other students have already written all the exciting topics, but this is far from the case. Time does not stand still, as well as discoveries. We analyzed the studies for 2023-2024 and found the most recent ideas for both undergraduate and graduate students. So let's explore exciting topics that will become interesting for the reader.
Political Science Topics
Politics is one of the most important research topics since it is it that underlies many processes taking place in society. The life and development of the entire country and people largely depend on who is in power. We have prepared good research topics about politics:
- Political Culture of the USA: Past and Present.
- Political risks and their management in the countries of Southern Europe and Latin America.
- Problems of the presidency and parliament.
- Opportunities and prospects for US foreign policy.
- The role of the media in the preparation and implementation of political transformations.
- The image of a political leader in the media.
- Religion and political conflict in the modern world.
- Political consultants and elections in Western countries: the example of the USA, Great Britain, France.
- Comparative historical analysis of presidential power in the United States.
- The political identity of a multicultural state (in the example of the USA, Canada, Australia, Great Britain, Germany, France).
- Impact of social media on political campaigns and voter behavior.
- Effectiveness of international institutions in promoting global cooperation and resolving conflicts.
- Role of electoral systems in shaping representation and political outcomes.
- Influence of interest groups and lobbyists on policy decisions and democratic governance.
- Relationship between economic inequality and political stability in democratic societies.
History Topics
History holds a special place in student education and is one of the most challenging topics for research. So check out the case study topics about which you can write a paper:
- Explore power in two empires: Assyria and Byzantium.
- What is the role of women in Britain back in prehistoric times?
- Do your research on Sumerian culture.
- Why did the people of Ancient Egypt believe in immortality?
- Franks: From the State of Clovis to the Empire of Charlemagne.
- Religion in the Middle Ages.
- How the knights lived?
- Spain under Arab rule.
- Education and development of the states of Central and Eastern Europe.
- India: land of treasures and wisdom.
- Impact of colonialism on societies in Africa.
- Role of women in the American Civil Rights Movement and their contributions to social change.
- Influence of the Renaissance on art, literature, and society in Italy and Europe.
- Origins and spread of Buddhism in Asia.
- Causes, consequences, and legacy of World War II on the international system.
Literature Topics
- How writers use psychology in literature?
- Analyze Don Quixote's personality.
- Art and Literature of Western Europe.
- Literature of America of the XX century.
- The best works of classic American literature.
- Literary History of Spain and Latin America.
- What do children from different countries of the world read in literature lessons?
- Three Centuries of American Literature: An Introduction to US Literary History.
- American Cultural Myths and Perspectives.
- 15 books by American writers that develop memory.
- Representation of gender in the works of Virginia Woolf.
- Portrayal of racial identity in the novels of Toni Morrison.
- Role of magical realism in contemporary Latin American literature.
- Impact of colonialism on postcolonial literature and its representation of identity and cultural hybridity.
- Use of mythology in the works of James Joyce.
Business Topics
- Marshall's Scissors: a symbol of the transition from classic to neoclassicism.
- Gossen's first and second laws or "pleasure theory".
- Bank guarantee as a tool to ensure the fulfillment of obligations.
- Currency risks and methods of their insurance.
- Adam Smith is the greatest English economist of the late 18th century.
- Economics Studies: Cambridge School.
- The era of the industrial revolution and its reflection in economic research D. Ricardo.
- USA in the world economy.
- Are taxes really the price we pay for the opportunity to live in a civilized world?
- What are the pros and cons of the process of globalization of the world economy?
- Impact of digital technologies on the customer experience and the future of e-commerce.
- Effectiveness of corporate social responsibility initiatives in improving consumer perception and brand loyalty.
- The effects of leadership styles on organizational culture.
- Implications of disruptive business models on traditional industries.
- Role of entrepreneurship in driving innovation and economic growth in emerging markets.
Education Topics
- Education as one of the main state priorities in the modern world.
- Education and its role in the development of society.
- Should the state finance training.
- During the classroom process, do teachers need to develop critical thinking in students?
- Throughout US history, education has evolved.
- How does modern technology affect education?
- What teaching approaches do teachers use?
- Which of the primary subjects each student should know.
- Is it necessary to put marks in modern teaching?
- What's best: learning online or offline?
- Impact of parental involvement on student academic achievement.
- The impact of teacher preparation programs on teacher effectiveness and retention rates in high-needs schools.
- Role of technology in transforming classroom instruction and enhancing student engagement and learning outcomes.
- Effects of standardized testing on curriculum and instruction.
- Relationship between educational attainment and economic mobility.
Psychology Topics
- The history of the development of psychology as a science.
- Basic scientific principles of psychology as a science.
- Perceptions and sensations as two primary forms of cognition of the surrounding world. Types of conflicts and ways of getting out of conflict situations.
- Providing psychological assistance to children in case of divorce.
- Theoretical and practical thinking in human life.
- Types of people's thinking and their specific manifestation.
- Factors contributing to personal self-realization.
- Authority and ways to maintain it.
- Psychological features of the emergence of Internet addiction.
- Impact of mindfulness meditation on anxiety and stress levels in college students.
- Effects of social media on self-esteem and body image in young adults.
- Influence of music therapy on the cognitive and emotional functioning of Alzheimer's patients.
- Effects of childhood exposure to nature on adult mental health outcomes.
- Psychological factors that contribute to online shopping addiction.
- Relationship between social support and resilience in trauma survivors.
Philosophy Topics
- The subject of philosophy. Basic questions of philosophy.
- World philosophy of the XX century: origins, main ideas, and directions.
- Myth and religion as preconditions for philosophy.
- The doctrine of God in the philosophy of Plato and Aristotle.
- Place and role of philosophy in culture.
- Philosophy and Medicine of Modern Times.
- Philosophy as a special way of knowing the world and its laws.
- Philosophical considerations of Pythagoras about numbers and the existence of the world.
- Emmanuel Kant and his philosophical views.
- Relationship of philosophy with other sciences.
- Ethical implications of gene editing and genetic engineering on future generations.
- The concept of free will and determinism in contemporary neuroscience research.
- Relationship between art and morality, and whether art can be morally right or wrong.
- Philosophical underpinnings of artificial intelligence and the ethics of AI decision-making.
- Intersection between philosophy and environmentalism, and the ethical considerations surrounding humanity's relationship with the natural world.
Medical Topics
- Biochemical features of blood composition in people of different body types.
- The influence of temperature on life processes.
- Game methods of work in speech therapy practice.
- Medical and psychological assistance to victims of environmental disasters.
- Medicine of the future, should all people get vaccinated?
- Features of medical ethics and deontology in therapy, surgery, obstetrics, etc.
- The heroism and courage of doctors during the Great Patriotic War.
- Hippocrates is an outstanding physician of antiquity. The modern meaning of the "Collection of Hippocrates.
- Galen is a physician of Ancient Rome, his experimental activities, and theoretical views.
- Modern medical techniques and their historical roots.
- Effects of telemedicine on patient outcomes and healthcare delivery.
- The impact of medical cannabis on symptom management and quality of life in cancer patients.
- Effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques in reducing chronic pain.
- Use of precision medicine to develop targeted therapies for genetic disorders.
- Relationship between gut microbiota and mental health, and the potential for therapeutic interventions to improve both.
IT Topics
- Information technology software.
- Evolution stages of information technology.
- Automated control systems for technological processes.
- Artificial intelligence information technology.
- Information technologies for information protection.
- Features of Adobe Photoshop.
- Modern computer graphics.
- Myths and realities of the Internet - known and hidden possibilities of the network.
- Advantages and disadvantages of working with a laptop, netbook, pocket computer.
- Signs of illegal entry into a computer system.
- Ethical implications of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms in decision-making.
- Impact of blockchain technology on financial systems and security.
- Effectiveness of phishing awareness training in preventing cyberattacks on individuals and organizations.
- Development of immersive virtual reality technologies for education and training purposes.
- Use of big data analytics in healthcare to improve patient outcomes and reduce costs.
Biology Topics
- Interaction between nature and society.
- Vitamins: types and their role in the human body.
- Proteins: chemical composition, properties, and significance for the human body.
- The role of medicinal plants in human life.
- Fundamental theories of human origin.
- Genetic engineering and its main problems.
- Photosynthesis is a unique natural phenomenon.
- Critically endangered animals.
- Types of races: features of their origin.
- Characteristic features of the regeneration process.
- Use of CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing to address genetic diseases and inherited disorders.
- Impact of plastic pollution on marine ecosystems and the potential for bioremediation strategies to mitigate its effects.
- Use of gene editing technologies to develop new cancer therapies.
- Development of artificial organs and tissues using stem cell engineering.
- Evolution of antibiotic resistance and the search for new antibiotics.
Create Your Theme If You Do Not Find a Suitable One
If you do not know how to choose a research topic, then first decide what you will write about. All topics for research work can be roughly grouped into three main groups:
- fantastic - themes focused on the development of non-existent, fantastic objects and phenomena;
- empirical - topics involving the conduct of their observations and experiments;
- theoretical - this group of topics focuses on the study and generalization of facts and materials in different sources. This is what you can ask other people; this is what is written in books, etc.
When creating a research topic, you need to adhere to the following rules:
- The topic should be interesting enough to make you want to deal with it for a long time. Research activity, like any creativity, is possible and effective only voluntarily. The desire to explore something arises when the object attracts, surprises, and arouses interest.
- The choice of the research topic should be based on existing knowledge, experience, and interest. The research topic should contribute to the maximum disclosure of the student's abilities, knowledge, interests.
- The research topic should be specific, and the problem being solved should be relevant.
FAQ Research Proposal Ideas
First Things First: What Research Proposal Is?
Research proposal - this is a purposeful study using scientific methods of phenomena and processes, the interaction between them, and analysis of the influence of various factors on them. Also, research can be defined as the study and development of new scientific or technological areas. Research is not always consumer-oriented and may not produce the result.
Everything matters when researching. Concentrating on the topic's primary or key issues, one cannot ignore the side facts, which at first glance seem insignificant. However, it is precisely such facts that may hide the beginning of important discoveries.
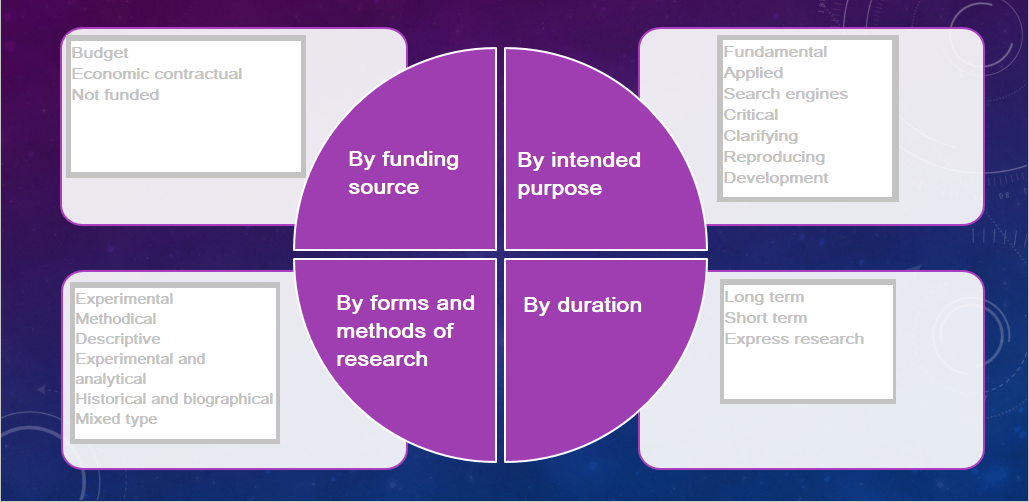
It is not enough for a researcher to establish a new fact. It is essential to explain from the standpoint of modern science, to reveal its general cognitive, theoretical, or practical significance. The presentation of scientific facts should be carried out in the context of the general historical process, the history of developing a particular industry and being multifaceted, considering general and specific features. Research classification:
How To Write a Research Proposal Correctly?
You are familiar with the research concept now; let's find out how to write proposal research. To write this task, you need to do several actions:
- Be clear about your research topic. Yogi Berra, a famous baseball player, once said, "If you don't know where you are going, you will end up in the wrong place." This statement has a lot to do with the research process. Try to formulate a straightforward question for your research from the beginning.
- To conduct research online, you need to use academic search engines. Our list of systems will save you time and effort:
- iSEEK Education
- RefSeek
- Microsoft Academic Search
- Keep the references for the sources. To avoid the trap of loss, save the information you need. If you're rubbing against a lack of information, spend time looking for new information, which will slow you down writing your research.
- Write a compelling introduction.
- Calculate the length of the paper. Before writing a study, check with the professor for the word count so that you don't redo unnecessary work.
- For each section, write your purpose. If this is an introduction, then fill in with the topic of the study. If this is the central part, then write about data, experiments. In the end, describe what you came to in your research.
- Create a list of used literature. To write a review of the literature, it is necessary to divide authors into groups. If they are chemists, then write them first, but do not mix them with other scientists, such as biology or physics.
What The Main Elements of The Research Proposal Include?
When you conduct research, it is assessed not only by how you described the theoretical part, but also the overall content of the document, how much information resources you used, and whether you structured the elements correctly. Research structure is how you express thoughts competently and consistently by dividing the text into chapters and paragraphs. And also, the article cannot do without graphs, tables.
The student's research paper should contain the following elements:
- Title page;
- Abstract;
- Introduction;
- The central part represented by chapters;
- Background;
- Questions of research;
- Research methods;
- Conclusion;
- References;
- List of symbols (if necessary).
The volume of all work should be 20-30 pages of good content. If you are writing text using Word and Google Docs computer programs, then use font size 12-14, Times New Roman; line spacing - 1.5-2; the size of margins: left - 30 mm., right - 10 mm., top - 20 mm., bottom - 20 mm. If you set all the parameters correctly, then, in the end, you will get a paper where you can write about 30 lines, and 60 characters will fit on one line, this is already with punctuation marks and spaces.
Title Page
The title page is the first page of the work and is filled according to strictly defined rules. The title page must contain the following information:
- full name of the educational institution in which the research work is carried out;
- the title of the work, which should determine the area of research carried out, be as short as possible and accurately correspond to the content of the research;
- surname, name of the student;
- name of the specialty;
- the genre of work, for example, final qualifying work;
- surnames, initials, scientific degrees, and titles of scientific adviser and reviewer;
- the city in which the educational institution is located;
- year of defense of the research work.
After the title page, a table of contents is placed, which lists all the research paper titles and indicates the pages from which they begin. The headings in the table of contents must exactly repeat the headings in the text. Headings must not be shortened or given in a different formulation or sequence. The table of contents should be placed at the beginning of the work, as this makes it possible to see its structure immediately.
Writing the Abstract
The abstract should reflect the purpose of the research, the main content, and novelty of the article compared to others, related in topic and purpose, and the results obtained. The abstract performs the following functions:
- makes it possible to establish the main content of a scientific article, determine its relevance and decide whether to refer to the full text of the paper;
- used in information systems, including automated systems for information retrieval.
The content of this paragraph should be consistent with the purpose of the annotation. Simultaneously, make the text concise, understandable, and try not to tire the reader with your data. Although this part is in front of the scientific article itself, it can be drawn up after working on the main content; then, you understand what to write about in the resume, because this is accurate information.
Introduction
In this part of the work, the chosen topic's relevance, goals, and objectives are briefly formulated. You also need to indicate the study's subject, what methods for the experiment you used, whether you got the results you expected, and whether these environments can apply in life. After you have formed the goals, write a hypothesis, this is a scientific proposition that concerns the experiment and will need to prove or disprove.
The introduction notes the signs of research novelty, its practical, theoretical, and social significance. Scientific novelty can be determined by the difference between the obtained results and the known ones. In this case, it is necessary to classify the degree of novelty and reveal the essence of new results.
The novelty of the results lies in the extent to which you could study the phenomenon and draw conclusions that have not been discussed by anyone before. You also need to explain why your results are useful for society and apply them to achieve positive discoveries. If you look from the other side, the novelty can be laid based on a new topic. For example, such experiments have never researched, scientists have never set such tasks before themselves, or have never put forward such hypotheses. At the end of the introductory part, it is essential to describe what structure the article has and what it is made of to navigate the text.
Main Part
In the chapters of the central part of the research work, an analysis of the theoretical material obtained from literary sources is given. The research methods and techniques are examined in detail, the practical part is highlighted, and the results are generalized. The central part of the research work is divided into chapters, paragraphs, points. Each element of the central part is a complete semantic fragment of the work. The central part of the work contains:
- review of literature on the topic and choice of research direction;
- description of sources of information;
- presentation of the general concept and primary research methods;
- the content of theoretical and experimental research;
- analysis and generalization of research results.
Your task in the central part is to demonstrate to the reader the research problem, why your hypothesis is essential, and what methods you used to prove its meaning. In the central part, we recommend using illustrations, such as pictures, graphs, diagrams, tables, so it will not look boring. If your text contains quotes, it is essential to indicate the source of the information so that the reader can not only find confirmation of the words but also do not take it for plagiarism.
Questions of Research
When starting a new research project, it is essential to develop sound research questions. This is an essential step as it will guide your research activities. Well-written research questions have several characteristics:
- they must be clearly defined and free from jargon;
- the questions should be focused enough to bring your research to its logical conclusion. It should summarize the unsolved problem that you want to investigate through literature study, experimental research, or theoretical work;
- they must be resolved within your limited time frame and other available resources (money, equipment, assistants, etc.).
Good research questions are not permanent. Don't be afraid to change your research questions, revisiting them as you study. For example, key data may be missing, or new research has been published that questions your premises.
What Research Methods Are There?
A huge number of research methods applicable in research work can be combined into methods of the empirical level, the experimental-theoretical level, and simply the theoretical level. Consider the possible research methods in a student's research project:
- Study of literature and other sources of information. This research method collects information on a research topic from books, magazines, newspapers, CDs, and the Internet. Before collecting information, it is necessary to highlight the basic concepts that are important for research and find their definitions.
- Observation - this research method is a purposeful perception of a phenomenon, during which the researcher receives information.
- Another method is polling. There are three main types of survey: conversation, interview, questionnaire. The conversation is conducted according to a pre-planned plan with the highlighting of questions requiring clarification. When conducting an interview, the researcher adheres to pre-planned questions, asked in a particular sequence. During the interview, the answers are recorded.
- Questionnaire - This research method is a massive collection of material using a questionnaire. Those to whom the questionnaires are addressed give answers to questions in writing.
- Experiment - This research method consists of conducting a series of experiments. An experiment includes creating certain conditions, observing what is happening, and fixing the results.
- Text analysis - this research method is a process of obtaining information through the interpretation of the text.
How To Describe The Approach?
This part takes 500-1000 words. In this section, you describe the steps taken to carry out the research and prove to the reader the validity of the methods chosen and the scientific validity of the results and conclusions drawn.
It is essential to describe each of the sections in as much detail as possible so that the reader clearly understands why you choose such research methods. This can achieve in the following ways:
- show that the research methods chosen are determined by the nature of the research object, the target population's nature, and the resources available. However, by no means cite resource constraints when researching a significant factor in methodological selection;
- show by providing links to relevant research papers that other researchers have used the same research methods in similar situations;
- indicate that from the theory of scientific research, the methods chosen are the best.
How to Write About Data Analysis Techniques?
Analyzing research data is a key step. It is a set of techniques and methods to check how to correct the assumptions and hypotheses and answer the questions asked. For a student, this is a difficult stage because, from professional qualifications, he will give accurate results and useful information.
Methods for analyzing social information fall into two large classes by how this information is presented:
- Qualitative methods focus on the analysis of information presented mainly in verbal form. In their pure form, they are usually used in the research of the idiographic type.
- Quantitative methods are mathematical and are techniques for processing digital information. Many of these methods are borrowed from the exact sciences, but some are specially developed by sociologists and psychologists to measure social phenomena.
How To Write About Research Results?
The purpose of the Results section is to present the data obtained after the study in an objective, systematic, and concise manner using text supplemented with illustrations. This section aims to present the results; interpretations or conclusions should not be included in this section. Therefore, this is one of the shortest sections in theory, but it can also be one of the most difficult sections.
This is because researchers often find it difficult to limit themselves to presenting the bare facts: they tend to include the explanations and inferences they draw from the results. This can make the Results section subjective, unclear, and confusing to the reader. You should present the data collected during the research as objectively, logically, and concisely as possible. Highlighting the most important results or organizing them into sections is an excellent way to show that you have covered all the information you need.
How Do I Insert Cite Sources?
The list of used literature is a list of information sources based on which the work was performed (cited, mentioned in the text, used in the research process, but not reflected in the work's main text). The list is made in alphabetical order.
If a student uses facts and quotes from other people in his work, he must write what material is taken. There is no need to add to the list those works that have not to use, but you consider them authoritative. This is a delusion for the reader. We also do not recommend specifying encyclopedias or information from journals in the bibliography. There is a separate place for them in the footnotes.
All materials that are not vital for understanding the scientific problem, auxiliary and additional materials that clutter up the central part's text are placed in annexes and notes. Take a look at the literature review example:

New Here? Get $5 OFF
Your First Project
We are a team of enthusiastic professionals and geeks in our field.
At the very start of the project
Money-Back Guarantee
Support 24/7
No Hidden Charges
Who Are the Experts?
Our experts are alumni from the world’s top universities and colleges.
All of them have successfully passed the Studybay examination and proven their competence to our team.
Our experts have graduated from the best universities in the world







Already Got Help? Write Your Review
👏